A WBS work breakdown structure is a project management tool that is planned to capture project activities in an illustrative diagram. The WBS was initially employed by the Defense Department of US, which directed its application on their projects. A work breakdown structure is not a list of tasks, a schedule or an organization chart. Rather it provides the basis on which a task list and a schedule can be constructed. Tasks and schedules are better handled in other ways, for example by using Gantt charts.
6 Implementing a WBS
The main purpose of a WBS is to keep track of the project’s scope, so you will need to add or remove elements as and when the scope of the project changes. Always make sure that the Work figure on the root branch is 100%. You can use the WBS to keep track of costs by adding figures for Budget and Actual as outlined above.
A WBS created with MindView also provides a good basis for preparing a task list and Gantt chart software for use by project management. To do this:
- Using a copy of the WBS document you have created, modify the branches so that they represent a task list. Remember, the WBS is not a task list but defines the scope of the project so it will need some modification before it reflects a proper task list. This typically involves rearranging the existing branches, deleting some and adding new ones. As MindView is designed for easy brainstorming these operations are straightforward.
- Switch to MindView's project management mode and the Gantt view.
- Enter the start date for the project.
- Link the tasks where appropriate so that start dates are, where possible, determined automatically by the end dates of preceding tasks.
- Add start dates to unlinked tasks.
- Add a duration for each task.
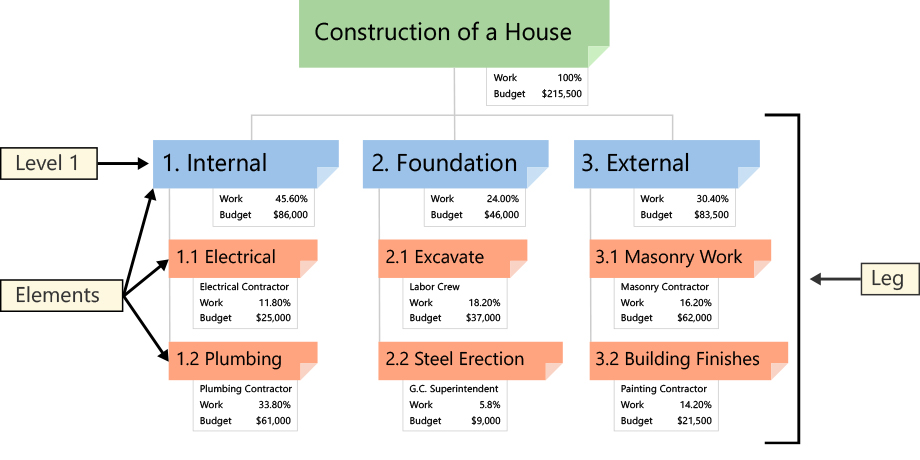
A Work Breakdown Structure (WBS) is a deliverable-oriented hierarchical decomposition of the work to be executed by the project team to accomplish the project objectives and create the required deliverables. A WBS is the cornerstone of effective project planning, execution, controlling, monitoring, and reporting. All the work contained within the WBS is to be identified, estimated, scheduled, and budgeted.
Work Breakdown Structure Diagram
The Work Breakdown Structure (WBS) is developed to establish a common understanding of project scope. It is a hierarchical description of the work that must be done to complete the deliverables of a project. Each descending level in the WBS represents an increasingly detailed description of the project deliverables.
The first two levels of the WBS (the root node and Level 2) define a set of planned outcomes that collectively and exclusively represent 100% of the project scope. At each subsequent level, the children of a parent node collectively and exclusively represent 100% of the scope of their parent node. Here is a Work Breakdown Structure example:
Quality of a Work Breakdown Structures
A well-designed WBS describes planned outcomes instead of planned actions. Outcomes are the desired ends of the project, such as a product, result, or service, and can be predicted accurately. Actions, on the other hand, may be difficult to predict accurately. A well-designed WBS makes it easy to assign elements of the WBS to any project activity. A good WBS should exhibit the following characteristics:
- Definable—can be described and easily understood by project participants.
- Manageable—a meaningful unit of work where specific responsibility and authority can be assigned to a responsible individual.
- Estimateable—duration can be estimated in time required to complete, and cost can be estimated in resources required to complete.
- Independent—minimum interface with or dependence on other ongoing elements (i.e., assignable to a single control account, and clearly distinguishable from other work packages).
- Integratable—integrates with other project work elements and with higher level cost estimates and schedules to include the entire project.
- Measurable—can be used to measure progress; has start and completion dates and measurable interim milestones.
- Adaptable—sufficiently flexible so the addition/elimination of work scope can be readily accommodated in the WBS framework.

Guidelines for Developing Work Breakdown Structure
The development of Work Breakdown Structure involves subdividing the major project activities or sub-activities into smaller, more manageable activities until the activities are defined in sufficient detail to support the management and development of project works. The items at the lowest level of a branch are known as work packages. Here are some tips in developing a Work Breakdown Structure that can express works effectively:

- Always express Work Breakdown Structure activities at the lowest levels of granularity in verb form.
- Review the Work Breakdown Structure. Make sure all deliverables have been fully covered by the works defined in the Work Breakdown Structure.
- Ensure that testing and training have been taken into account.
- Ensure that non-IT work packages are also included such as, documentation and review activities are included in the structure.
- Ensure that other supporting activities such as, product/service launch and implementation activities are planned.
- Ensure that delivery approval cycles are taken into account.
- Include project management deliverables on the project as well (e.g. production of Project Plan). Include any deliverables that must be met or delivered by the customer or any external parties. Check the Work Breakdown Structure against the project approach specified in Project Charter for any activities that needs to be included in the Work Breakdown Structure.
Different Forms of Work Breakdown Structure
Generally speaking, there are three typical ways in structuring works with a Work Breakdown Structure (WBS). They includes phase-based structures, deliverable-based structures and responsibility-based structures.
Phase-based structures
Define and structure project activities based on the project phases.

Deliverable-based structures
Define and structure project activities based on the deliverables agreed to deliver.
Responsibility-based structure
Define and structure project activities based on the organization units that will work on the project.
Other Use Cases of Breakdown Structure
Typical use of breakdown structure as a project management tool includes Work Breakdown Structure (WBS), Resource Breakdown Structure, Risk Breakdown Structure and Organization Breakdown Structure (OBS), or sometimes known as Organization Chart.
Resource Breakdown Structure
Resource Breakdown Structure (RBS) is a project management tool that provides a hierarchical decomposition of resources, either structured by resource category, types or by IT/business function that has resource needs.
Here is a Resource Breakdown Structure example:
Risk Breakdown Structure

Risks are everything in any IT project. The existence of risk causes negative impact on project schedule, costs and quality. In project management, Project Manager is responsible for managing risks and to ensure that the project will be delivered on time, within project and up to the standard user expected. One of the popular risk management tool is the Risk Breakdown Structure.
Risk breakdown Structure is the hierarchical decomposition of risks, starting from the root node element that represents the project, and going down to the various risk categories, and then finer level risks.
Besides presenting project risks in a Risk Breakdown Structure, it is possible to combine the use of Color Legend in representing the impact of risk. Take a look at the Risk Breakdown Structure example below, a legend of Impact with five items has been setup, representing the five levels of impacts that risks may have on the project with five distinct color code.
Here is a Risk Breakdown Structure example:
Wbs Work Breakdown Structure Wikipedia
Organizational Breakdown Structure
Organizational Breakdown Structure, or sometimes known as Organization Chart, is a widely used project management tool for representing project organization. It typically begins with the project sponsor, and with all key stakeholders included. In presenting the organization structure, consider the organization or group that is requesting the project and the level of their sponsorship and authority.
Deliverable Based Work Breakdown Structure
Here is an Organizational Breakdown Structure example: